Robotics Process Automation 101
Robotics Process Automation 101
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), although initially developed in the late 1990s, emerged as a practical technology in the early 2000s. RPA is defined as “a form of business process automation technology based on metaphorical software robots or digital workers.” RPA is sometimes referred to as software robotics. The term RPA was coined by Blue Prism, to describe technology that interacts with a digital workforce by following rule-based business processes. Systems that utilize RPA are intended to interact with organizations in the same way existing users do, eliminating the need for workers to perform labor-intensive tasks associated with their assignments.
The Growth of Robotics Process Automation
The RPA market has seen significant growth in the last few years and has been implemented across various industries and departments. Forrester, an American market research company, has predicted the RPA software market will grow to $22 billion in 2025. Today, RPA can be seen in IT, HR, Finance & Accounting, and Engineering, particularly in electronic document management systems. RPA is anticipated to drive growth in the coming years by integrating with technologies such as speech recognition, machine learning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Artificial Intelligence (AI). RPA was first adopted by the financial industry to automate records from monetary transactions but has rapidly made its way into the engineering space. Engineering managers quickly realized the potential of RPA for managing workflows and project data. The possibilities fueled by RPA are seemingly limitless, which is why experts predict the RPA industry is expected to reach $3.11 billion by 2025.
93% of businesses plan to deploy RPA by 2023
Source: Deloitte
Robotics Process Automation for Engineering
Robotic Process Automation can best be seen in engineering document management systems (EDMS) in the way they facilitate design, drafting, and collaboration workflows. Systems utilizing RPA manage repetitive, labor-intensive tasks using rules-based logic, determined by IT managers and/or EDMS administrators and project managers. In addition, many of these systems are equipped with project tracking features, to manage and control the speed in which these workflows are completed. As a result, software robotics has become synonymous with efficiency and cost reduction, since task automation can virtually eliminate human error and assists in reducing arduous manual tasks. According to Software Testing and Big Data Hadoop, approximately 10 to 20 percent of human work hours are spent on dull, repetitive computer tasks.
RPA systems help AEC (architecture, engineering, and construction) companies include third parties in their workflows and thus improving project outcomes. Additionally, it allows these companies to spot inefficiencies that may adversely affect project completion times and unnecessary costs.

eQuorum’s EDMS as RPA
Although RPA systems may sound complicated to use, they actually aren’t. With a constantly changing economic landscape and increase in remote work, it is critical teams have the right tools to work together more effectively and to solve problems, both internally and with third parties. As work teams become more distributed and file security more concentrated, having applications, like RPA, that assist in getting the right information to the right workflow participants at the right time becomes even more important.
Our engineering workflow and document management system uses RPA to automate workflows, file distribution, metadata changes, notifications, and more. It’s an affordable solution for organizations looking to implement RPA, to see a quicker return on investment while simplifying collaboration between external and internal teams. Additionally, our EDMS includes basic Artificial Intelligence (AI) such as metadata search and we’ll be growing its AI capabilities over the next few years. Now, ImageSite and Engine-Box, address some of the easiest processes to automate, and are a must-have for small to medium-sized businesses or even large corporations. Our engineering workflow and document management systems are designed to save time, reduce human error, and save your organization money while maximizing resource utilization. In fact, many of our customers have seen a return on investment in as little as four months.
Our engineering workflow and document management system have the following RPA capabilities:
- Managing repetitive, labor-intensive tasks
- Task tracking and audit trails
- Automatically updating file status as changes are made to project timeline
- Validating data and verifying users
- Downloading and updating files
- Analyzing and extracting data
- Searching databases
- Monitoring data, users, and activity.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) vs Artificial Intelligence (AI)
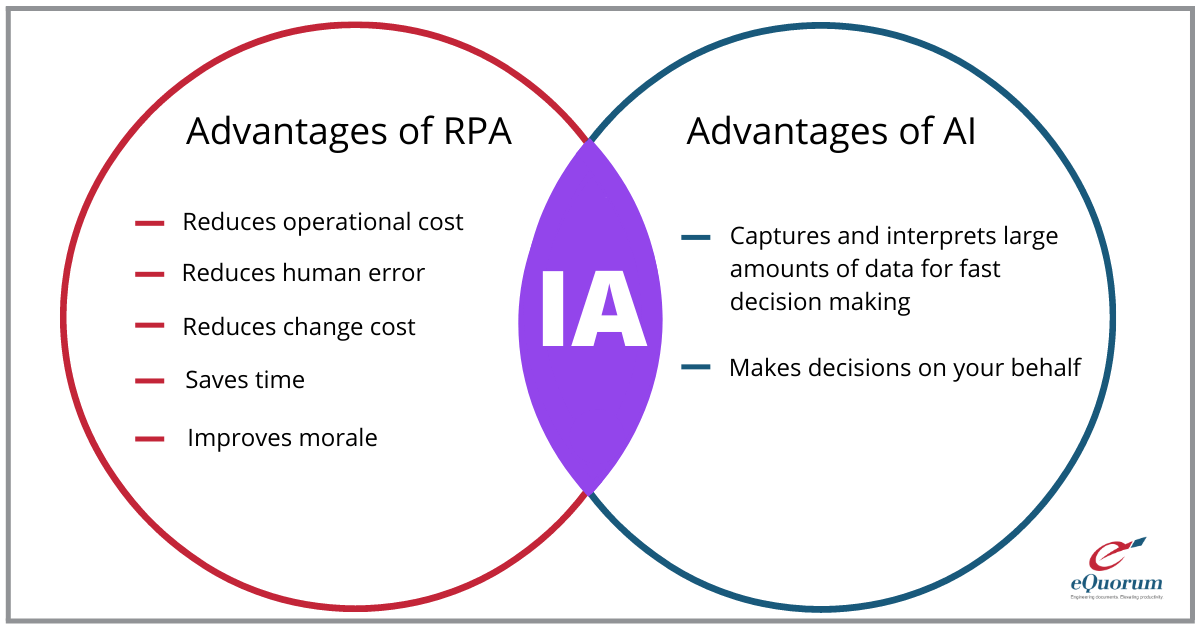
A common misconception is that Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence are the same. While RPA and AI possess similar qualities, they have a variety of different functions and applications. RPA is primarily used to manage repetitive tasks that are structured, rigid, or tedious. Artificial Intelligence, on the other hand, is used to make judgement calls that go beyond basic rules and configuration. It is used as an umbrella term for software that imitates the human ability to sense things, while RPA is used to eliminate job work for the sake of efficiency. To put it simply, RPA is programmed by the user, whereas AI programs itself. (Although some RPA applications are embedding in AI capabilities more and more.) RPA and AI can be used in conjunction with one another using the right combination of systems. In this case AI would collect and interpret data that would then be used to automate repeatable tasks. This is rare, however, since AI is still a fairly new technology, that has not yet been perfected.Intelligent Automation
Intelligent Automation (IA) is the combination of Artificial Intelligence, RPA, and machine learning. Intelligent Automation differs from RPA, since it incorporates added layers of machine learning and AI. Functions of IA can range from gathering data to making decisions about visual or textual information. Intelligent Automation is used for a wide variety of applications and can be seen in many of the autonomous vehicles that are being developed.
Summary
The explosion of Robotic Process Automation is changing the way we interact with software. It has the potential to increase efficiency, reduce error, and improve the overall well-being of employees. Various systems use RPA to make life easier for organizations and their employees, in industries ranging from engineering to finance and more. RPA can be combined with artificial intelligence to further increase efficiency in document control systems. RPA is a quick and simple way to reduce costs and eliminate unnecessary tasks from your employee’s workload. Though it’s a relatively new technology, it is now being widely adopted by corporations around the World.
Additional EDMS Features
Our EDMS solutions
ImageSite and EngineBox are eQuorum’s robust workflow and document management solutions, created to help workers manage their essential workflows while maintaining complete control over their engineering files and documents. Not only do they provide a secure collaboration site for workers, but they also help organizations manage document distribution with third parties like vendors, contractors, and customers. Both systems are offered at a competitive price, enabling organizations to get a quick return on their investment by providing the features and functionality needed to help organizations improve efficiency, productivity, and collaboration. Companies can choose from concurrent user subscriptions or named user subscriptions, ensuring organizations have subscription options that make sense for their business.
ImageSite®
Our single source engineering workflow and document management system. Built in HTML5 so there is no software to deploy to client computers or mobile apps to download. Offered as an On-premise or Private Cloud system.
EngineBox™
EngineBox is a cloud based workflow and document management version of ImageSite that resides outside the corporate network.
Our EDMS solutions
ImageSite and EngineBox are eQuorum’s robust workflow and document management solutions, created to help workers manage their essential workflows while maintaining complete control over their engineering files and documents. Not only do they provide a secure collaboration site for workers, but they also help organizations manage document distribution with third parties like vendors, contractors, and customers. Both systems are offered at a competitive price, enabling organizations to get a quick return on their investment by providing the features and functionality needed to help organizations improve efficiency, productivity, and collaboration. Companies can choose from concurrent user subscriptions or named user subscriptions, ensuring organizations have subscription options that make sense for their business.
EngineBox™
EngineBox is a cloud based workflow and document management version of ImageSite that resides outside the corporate network.
The eQuorum Customer Promise
In 2005, eQuorum developed the first all browser-based EDMS. The system, although for on-premise use, was still created to remove client software and JAVA from user computers and allow users to have a single viewer based on the simple navigation functionality of browsers. Today, eQuorum provides that same application in a private Cloud or a SaaS Cloud option. We can do this because we are, and have always been, browser-based, understanding the enhanced speed, security, and usability of this technology.
With the abundance of document management systems on the market today, there’s no doubt that choosing the right Cloud document management software can be a difficult decision. eQuorum is here to provide a comprehensive, powerful, and most importantly – affordable Cloud document management solution. We believe in providing real value to our customers by eliminating unnecessary costs, providing industry-leading functionality, and equipping your team with the right tools using cutting edge technology to bring your products to market faster.
eQuorum®
We specialize in engineering workflow and document management. Our comprehensive, yet easy-to-use software provides the solution to manage data from design to manufacturing and production, to sales, support and administration.